Appearance
【2D矩阵】
数学意义
应用于物体的平移、旋转、缩放、坐标系变换。
2D矩阵变换
缩放
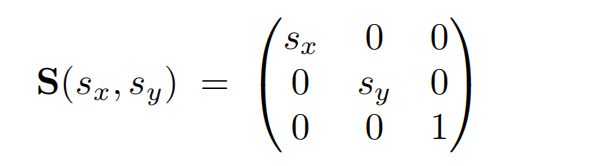
旋转
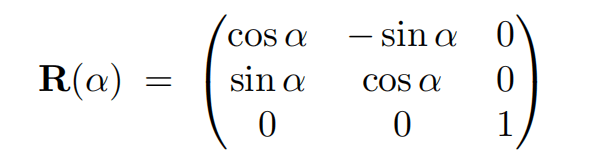
glsl
// OpenGL里使用矩阵旋转uv示例
vec2 rotate(vec2 uv,float a)
{
mat2 mat = mat2(cos(a),-sin(a),sin(a),cos(a));
vec2 uv2 = uv - 0.5;
vec2 uv3 = mat * uv2;
return uv3 + 0.5;
}平移
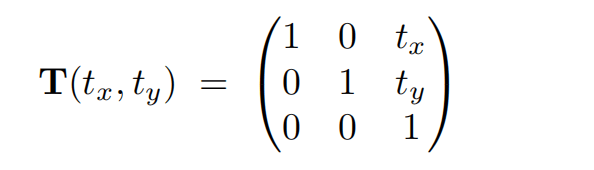
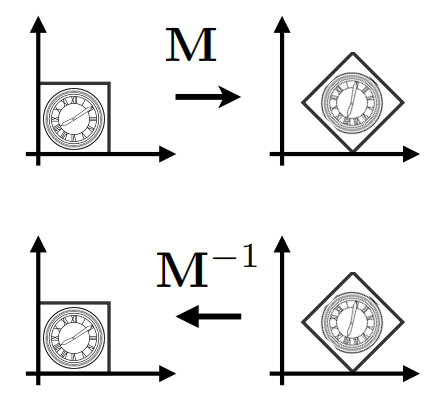
逆矩阵
逆矩阵可以让变换进行反向操作。
矩阵合并
可以让移动、旋转等进行合并成一个矩阵,使用合并后的矩阵,能直接让指定向量进行变换。
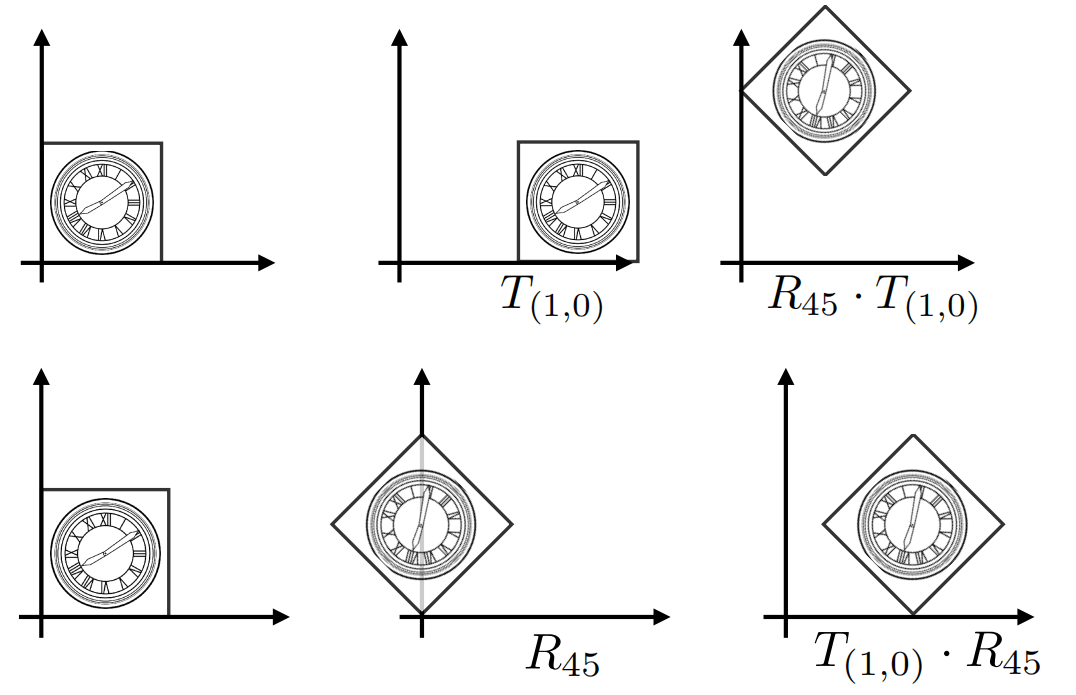
观察上面两种不同的矩阵相乘,可以发现,矩阵的乘法不具有交换律。先移动再旋转和先旋转再移动的结果是不一样的。
注意,先移动再旋转,向量乘法里的矩阵顺序是相反的,既 旋转M X 移动M。
齐次坐标
2d矩阵是3X3的,增加一个维度是为了处理移动。

一个2d数据加一个维度变成3d数据,是有意义的。 其中前面两个是x与y,第三个数据表示该数据是否是点(否则是向量)。 这么理解有个重要的性质:
- 向量 + 向量 = 向量
- 点 - 点 = 向量
- 点 + 向量 = 点
- 点 + 点 = 两个点之间的中间点
2D矩阵示例
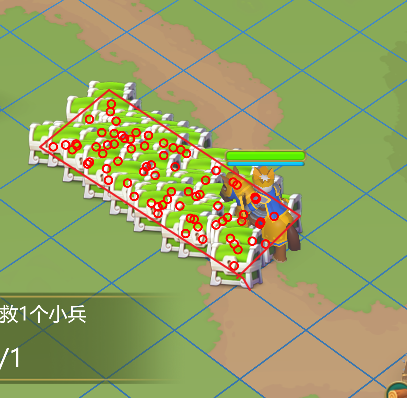
比如技能的矩形选择区域
javascript
export abstract class BaseShapeSelector {
/** 位置 */
position: Laya.Vector2 = new Laya.Vector2();
/** 方向 */
direction: Laya.Vector2 = new Laya.Vector2();
/**
* 设置Transform里的rotation 角度制
* Transform里的rotation 值范围在 -360 ~ 360 之间
* 180°
* ↑
* 270°←→90°
* ↓
* 0°
*/
setRotation(rotation: number): void {
if (rotation < 0) rotation = rotation + 360;
if (rotation > 360) rotation = rotation - 360;
rotation = (rotation / 180) * Math.PI; // 0 ~ 2PI
this.direction.x = Math.sin(rotation);
this.direction.y = Math.cos(rotation);
}
/** 检查指定位置是否在内部 */
abstract checkInternal(target: Laya.Vector2): boolean;
}
/** 矩形区域选择器 */
export class RectShapeSelector extends BaseShapeSelector {
/** 距离,同长度 */
distance: number = 0;
/** 宽度 */
width: number = 60;
private mat2D_T: Laya.Matrix3x3 = new Laya.Matrix3x3();
private mat2D_R: Laya.Matrix3x3 = new Laya.Matrix3x3();
private mat2D_TR: Laya.Matrix3x3 = new Laya.Matrix3x3();
/** 目标点在矩形内的局部坐标 */
private targetInRect: Laya.Vector2 = new Laya.Vector2();
private resetPos: Laya.Vector2 = new Laya.Vector2();
checkInternal(target: Laya.Vector2): boolean {
this.direction.normalize();
const rad = Math.atan2(this.direction.y, this.direction.x);
this.resetPos.x = -this.position.x;
this.resetPos.y = -this.position.y;
Laya.Matrix3x3.createFromTranslation(this.resetPos, this.mat2D_T); // 平移到原点的矩阵
Laya.Matrix3x3.createFromRotation(-rad, this.mat2D_R); // 旋转到水平的矩阵
// 先平移到原点再旋转到水平,矩阵乘法操作是相反的,即旋转矩阵乘以平移矩阵
Laya.Matrix3x3.multiply(this.mat2D_R, this.mat2D_T, this.mat2D_TR);
// 把 target 世界坐标位置转换为矩形内的局部坐标。
Laya.Vector2.transformCoordinate(target, this.mat2D_TR, this.targetInRect);
// 判断局部坐标是否在矩形外,是则返回false
if (this.targetInRect.x < 0) {
return false;
}
if (this.targetInRect.x > this.distance) {
return false;
}
if (this.targetInRect.y > this.width / 2) {
return false;
}
if (this.targetInRect.y < -this.width / 2) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
/** 扇形区域选择器 */
export class FanShapeSelector extends BaseShapeSelector {
/** 距离,同半径 */
distance: number = 0;
/** 扇形角度0~360 */
angle: number = 60;
/** position 指向 target 的向量 */
positionToTarget: Laya.Vector2 = new Laya.Vector2();
/** 检查指定位置是否在该扇形区域内部 */
checkInternal(target: Laya.Vector2): boolean {
const distance = Laya.Vector2.distance(this.position, target);
if (distance > this.distance) {
return false; // 距离超出了扇形
}
this.positionToTarget.x = target.x - this.position.x;
this.positionToTarget.y = target.y - this.position.y;
this.positionToTarget.normalize();
this.direction.normalize();
// 半角度
const halfAngle = this.angle / 2;
const dotVal = Laya.Vector2.dot(this.direction, this.positionToTarget);
// 指向目标,与指向当前对象构成的夹角
const angle2 = Math.acos(dotVal); // 0~2PI
// angle2 转换成角度
const angle2Degree = angle2 * (180 / Math.PI);
if (angle2Degree > halfAngle) {
return false; // 目标在扇形外
}
return true;
}
}